Final Project
Posted in EdTech506, Final on 3:16 PM by Jes CaronOrganization - Unit 5 Final Take
Posted in Final, Unit 5, Usability on 2:44 PM by Jes Caron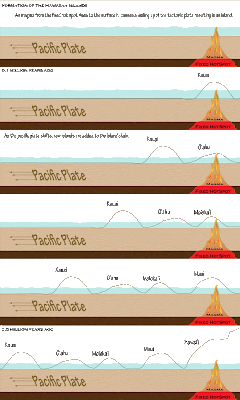
Organization - Unit 5 Take 2
Posted in EdTech506, Unit 5, Usability on 3:48 PM by Jes Caron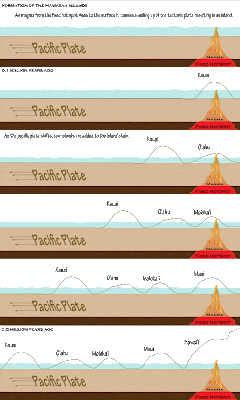
Unit 5 - Discussion of Wordle
Posted in Discussion, EdTech506, Wordle on 1:16 PM by Jes CaronThesis in a Cloud

I am including the abstract from my thesis below in case anyone is interested :)
Due to the serious risks associated with estrogen therapy following menopause many women are turning to a natural alternative, phytoestrogens. Phytoestrogens are plant derived compounds which induce estrogenic response in humans. Estrogenic response is produced by phytoestrogens interacting directly with the estrogen receptor. The estrogen receptor is a steroid receptor belonging to the nuclear receptor family, which has high affinity for both its native ligand 17β-estradiol and phytoestrogens.
Many women seeking to avoid the drawbacks of estrogen therapy opt to “safely and naturally” relieve menopausal symptoms with over the counter phytoestrogen supplements. While anecdotal evidence suggests phytoestrogen supplements do indeed provide menopausal relief the true risk to the individual has yet to be assessed. The goal of this project was to assess the effects of an OTC phytoestrogen supplement, Promensil®, on the proliferation of an ER positive neoplastic breast epithelial cell line, MCF-7.
Exposure to 100% Promensil® extract caused a marked decrease in cell growth relative to control over all assay systems used; MTT, tritiated thymidine uptake, and PCNA immunoblotting. Reduction in cellular growth was accompanied by an upregulation in the caspase pathway, as evidenced by the presence of procaspase-3 banding in phytoestrogen treated cells. While further investigation is warranted, a reduction in the growth of ER positive neoplastic breast epithelial cells through the use of phytoestrogens could prove to have real life clinical implications. Defined phytoestrogen mixtures may prove to be potential drug candidates for the prophylactic treatment of women at high risk for breast cancer.
Organization - Unit 5 Take 1
Posted in EdTech506, Unit 5, Usability on 6:07 PM by Jes Caron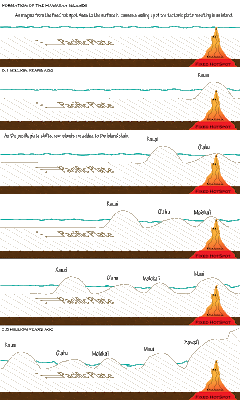
Color and Depth - Unit 4 Final Take
Posted in EdTech506, Final, unit 4, Usability on 5:25 PM by Jes Caron
Color and Depth - Unit 4 Take 2
Posted in EdTech506, unit 4, Usability on 5:13 PM by Jes Caron Based on comments provided by my partner I have modified the positions of the snails to place them all in the same plane relative to the ground. Placing all the snails in front of the ground enhances the feeling that the snail is moving forward along the ground. It also limits issues with figure ground that may have resulted from the previous orientation of the snails. It was also suggested that a bit of bevel be added to the last snail which is a suggestion that I like a lot, however due to the way my figure was drawn the addition of a bevel in Illustrator does not appear to be possible.
Based on comments provided by my partner I have modified the positions of the snails to place them all in the same plane relative to the ground. Placing all the snails in front of the ground enhances the feeling that the snail is moving forward along the ground. It also limits issues with figure ground that may have resulted from the previous orientation of the snails. It was also suggested that a bit of bevel be added to the last snail which is a suggestion that I like a lot, however due to the way my figure was drawn the addition of a bevel in Illustrator does not appear to be possible.


